First Person: Telling the tragic story of mercury poisoning in Japan
 Masami Ogata is a survivor of Minamata Disease, a debilitating illness caused by industrial mercury poisoning, which originated in the Japanese town of the same name in the 1950s. As a UN conference on preventing future poisoning outbreaks gets underway, we hear Mr. Ogata’s story.
Masami Ogata is a survivor of Minamata Disease, a debilitating illness caused by industrial mercury poisoning, which originated in the Japanese town of the same name in the 1950s. As a UN conference on preventing future poisoning outbreaks gets underway, we hear Mr. Ogata’s story.
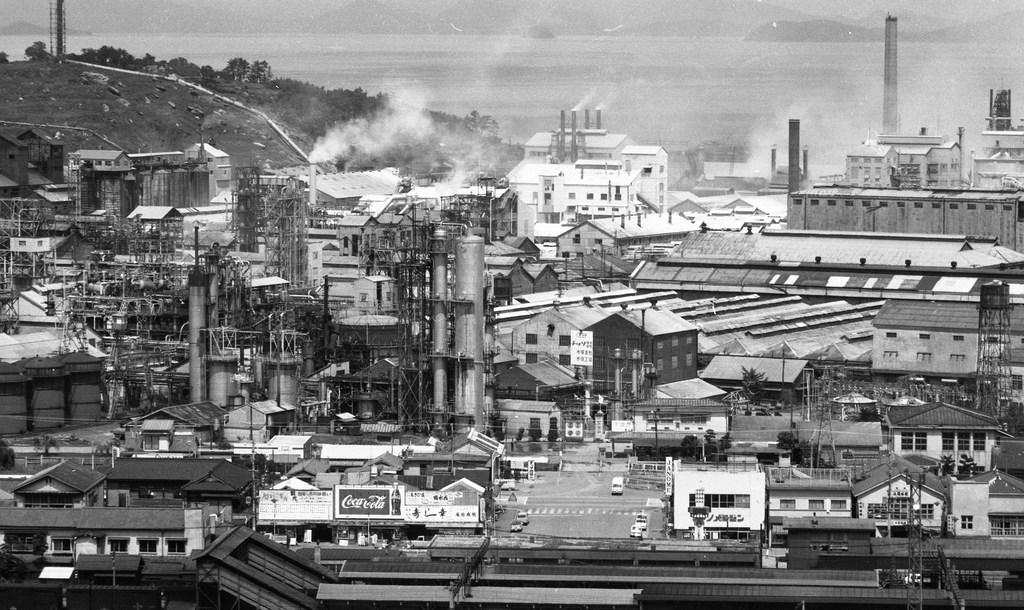
As a storyteller at the Minamata Disease Municipal Museum, Mr. Ogata helps to keep alive the memory of what is considered to be one of the most serious Japanese pollution incidents of the Twentieth Century.
The incident was caused by the release of toxic chemicals from an industrial plant, which accumulated in shellfish and fish, and were then eaten by the local population.
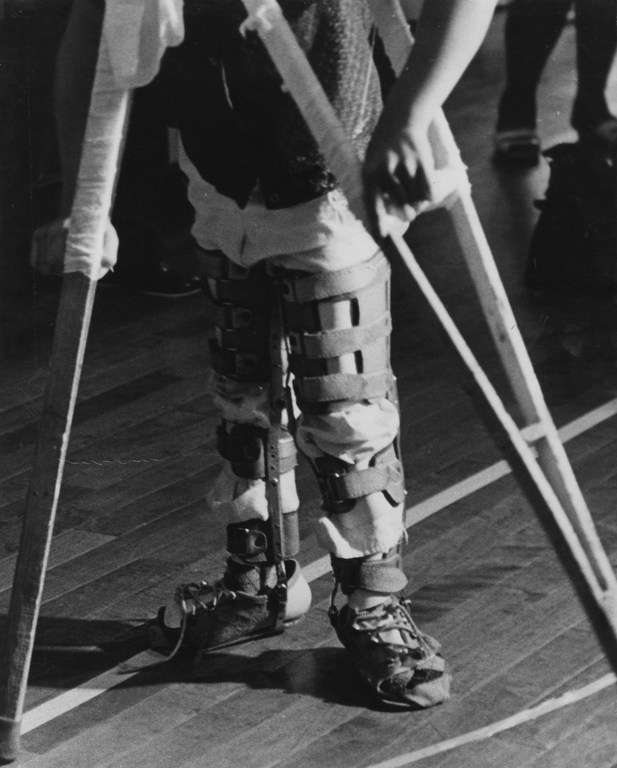
More than 2,000 people have been recognized as victims, many of whom, including Mr. Ogata, had to fight for recognition and compensation: around 20 members of his family were affected by the disease, which causes muscle weakness, loss of peripheral vision, and hearing and speech impairment.

Minimata Disease Municipal MuseumMasima Ogata, a storyteller at the Minimata Disease Municipal Museum in Japan, who lives with the disease.
“Minamata disease first caused damage to my family in September 1957. When I was nearly two years old, my grandfather Fukumatsu Ogata suddenly developed an unexplained illness, which worsened day by day, with convulsions and drooling, difficulty walking, speech problems, and other symptoms.
 Minimata Disease Municipal MuseumMinamata Disease is a neurological disease caused by severe mercury poisoning.
Minimata Disease Municipal MuseumMinamata Disease is a neurological disease caused by severe mercury poisoning.
Two months later, he passed away in the isolation and infectious diseases ward at the Minamata City Hospital. That was the first tragedy caused by Minamata disease in the Ogata family. However, we were never told what caused the illness. My sister Hitomi, who was born a week before her grandfather developed the illness, was born with a disability, again without explanation, then other members of the Ogata family started falling ill one after another.
When I became an adult, I noticed that I had very little sensation in my limbs. I work as a joiner and, when I was younger, would often cut my finger on the whetstone when sharpening knives, because my finger would droop.
We came to understand that it was caused by methyl mercury poisoning but we couldn’t really make it public that we were victims, because people thought that Minamata disease was contagious.
Rumours spread though, and people would say that no one should marry a member of the Ogata family. I got married at the age of 20, but on the day of our engagement, my wife had a phone call. Naming me, the person said to her, “the man you are trying to marry is a Minamata disease victim. The whole family will be annihilated. Are you okay to go to such a place as a bride?”
When I was younger, I hid my disease from others. I would change the subject if it came up, and say that it had nothing to do with me. It was my daughter who said to me that I had to live honestly. Her words stuck in my chest, and I chose to stop hiding, at the age of 38.
For 10 years, my application to be officially declared a Minamata disease victim was rejected until, on March 15, 2007, the Governor of Kumamoto Prefecture declared that she would recognize me as a Minamata disease patient.
After receiving the certification, I asked myself how I would live in the future, then I decided to become a storyteller, so that I could tell people all over the world about the disease.
Minamata, which has suffered so much, has adopted the UN Convention named after the city, which will save the lives of many people around the world. The people of Minamata suffered a lot from the disease and were torn apart, but from that we gained a wonderful power, in the form of the Minamata Convention.
Minamata disease is by no means over but, by showing people around the world what victims can do and achieve, I think the world can take courage.”
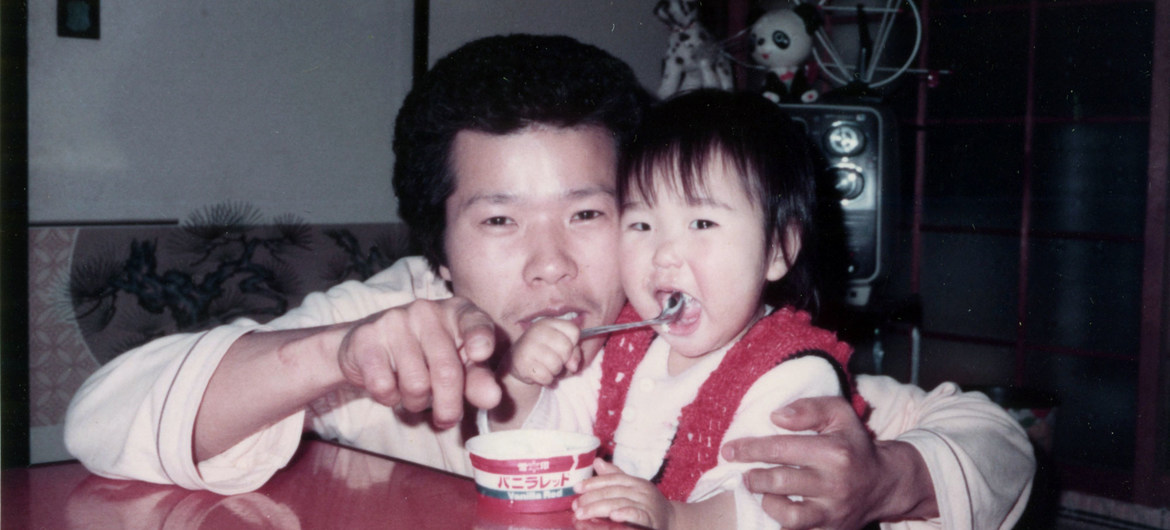

Minimata Disease Municipal MuseumMasima Ogata, a storyteller at the Minimata Disease Municipal Museum in Japan, who lives with the disease.



